Infectious Agent
An agent capable of producing infection.
Example: Bacteria, Virus, Fungus, Protozoa, Helminth
Reservoirs
Is the breeding ground for bacteria/viruses.
Somewhere which contain proper nutrients and suitable environment.
Example: Humans, Animals, Environment, Formites
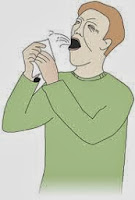
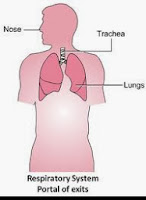
Portal Of Exit
Is the path by which a pathogen leaves its host.
Through respiratory tract (nose, mouth), intestinal tract (rectum), urinary tract, or blood and other body fluids.
Example: saliva from the oral cavity,sneezing,coughing,faeces from the bowel,vomits, infected blood and wound.
.jpg)
.jpg)
Means Of Transmission
An organism transfers from one carrier to another by either direct transmission or indirect transmission. 1.Direct Transmission
- Person-to-person transmission of pathogens through touching, biting, kissing, or sexual intercourse.
- Example: expelled from the body by coughing, sneezing or talking
- Organisms travel in droplets over less than 1 metre in distance and are inhaled by a susceptible host.
2. Indirect Transmission
- The transfer of an infectious agent from a reservoir to a host by suspended air particles, inanimate objects (vehicles), or animate intermediaries (vectors).
- Airborne transmission occurs when infectious agents are carried by dust or droplet nuclei suspended in air.
- Vehicles that may indirectly transmit an infectious agent include food, water, biologic products (blood), and fomites (inanimate objects such as handkerchiefs, bedding, or surgical scalpels).
- Vectors such as mosquitoes, fleas, and ticks may carry an infectious agent through purely mechanical means or may support growth or changes in the agent.
Portal Of Entry
Opening where an infectious disease enters the host’s body such as mucus membranes, open wounds, or tubes inserted in body cavities like urinary catheters or feeding tubes.
Susceptible Host
Person who is at risk for developing an infection from the disease.
Example: someone who had low immunity, old people, children
.jpg)
2. Explain ten (10) nursing interventions to break the chain of infections.
A. Change client linen every morning.
R: To reduce the microorganism in client's room.
B. Appropriate handling and disposal of body secretions like vomitus, faeces, sputum, blood and body fluids.
R: To prevent the spread of infection/microorganism.
C. Apply effective hand washing.
R: So that nurses won't carry the microorganism to another client.
D. Cover your mouth and nose when coughing and sneezing.
R: To stop the microorganism from spreading out to others.
E. Do exercise at least three times a week.
R: To maintain the health of the body.
F. Eat a proper nutrition.
R: To have a good immune system.
G. Wear gloves when cleaning the wounds.
R: To prevent microorganism/body fluids from entering/touching the skin.
H. Throw away needles in the clinical waste bin after used.
R: To prevent the needles cut others person.
I. Throw away the facial tissue once you used.
R: To prevent the fluids that contain microorganism flow to another person by touching it.
J. Wear full PPE which is gloves, masks, gowns, and goggles when entering isolation room.
R: To prevent the microorganism flows to use through airborn infection.

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
ALl Of I NEdd Is Here
ReplyDelete